Java Explained
 In simple terms, Java is a programming language that is used to create software programs. In other words, it’s the underlying technology for business applications, games, PC utility tools, and more. As of 2012 it has been used for client-to-server web applications by over 10 million users. One reason for its popularity is that it is a simplified language that was designed to eliminate common programming errors. It was also designed for programmers to “write once, run anywhere” – that is, the code needs only to be written once to be able to run on computers with different operating platforms. Technically more than a programming language, Java is also a platform for developing applications. This means that programmers do not have to be concerned if the application is running on a Mac, PC, or Linux. If the Java components, also known as runtime environment, are available, it will run as expected.
In simple terms, Java is a programming language that is used to create software programs. In other words, it’s the underlying technology for business applications, games, PC utility tools, and more. As of 2012 it has been used for client-to-server web applications by over 10 million users. One reason for its popularity is that it is a simplified language that was designed to eliminate common programming errors. It was also designed for programmers to “write once, run anywhere” – that is, the code needs only to be written once to be able to run on computers with different operating platforms. Technically more than a programming language, Java is also a platform for developing applications. This means that programmers do not have to be concerned if the application is running on a Mac, PC, or Linux. If the Java components, also known as runtime environment, are available, it will run as expected.
- The Java website estimates that it runs on more than 850 million PCs across the globe and billions of devices such as mobile and TV devices.
- Java is unrelated to JavaScript, though either can be used to enable the functioning of web pages.
- Sun Microsystems first developed Java with five primary goals in mind:
- Simple, object-oriented and familiar.
- Robust and secure.
- Architecture-neutral and portable.
- High performance.
- Interpreted, threaded, and dynamic.
In short… it was designed to be flexible and powerful while still being secure. Also it was to be portable across multiple architectures, operating systems, and graphical user interfaces. You can see it on computers, laptops, gaming devices, cell phones, and on websites. As the Java website states: “Java is everywhere”.
To Have or Have Not
There are many Java skeptics who are trying to cut back on their Java intake… or eliminate it altogether. The reason for this is that, like any programming language, Java can be exploited by those wanting to take advantage of security loopholes. We will discuss the issue of security here. But first we will point out what to expect if you remove Java altogether.
Without Java: If you turn off Java (remove it from your PC world), and you come across websites that have Java apps embedded within, you will see a blank space where the program applet would be displayed. Also… as pointed out by its website, without Java applications and websites that depend on it will not work. Despite this, some experts are now saying the use and dependency on Java is declining somewhat. There are alternatives to Java such as HTML5. There are also some that declare Java to be unsafe and a security threat. It certainly has had its share of bugs.
Security Risk: Here is a quick peek at some of the recent issues that have hit Java.
- August 2012: Researchers at the Polish security firm Security Explorations say they’ve found yet another bug in Java–this time in the patch intended to fix a set of security issues in the software through a critical update released just a day before. The researchers, who were also the first to report the initial security problems in Java more than four months ago, say this new vulnerability in the ubiquitous plugin is capable of allowing the same invisible downloads of malware onto victims’ computers via their web browsers. The possible outcome is that the vulnerabilities could be used to exploit personal data and accessibility of the user’s system overall.
- January 2013: Oracle has issued an emergency fix for its Java software, which security experts said is being exploited to carry out identity theft and other crimes — but flaws remain which can still be exploited, researchers say. The fix… is intended to block an exploit in Java from running in web browsers… When used on websites, Java is typically used to run small apps that are loaded from inside the browser, but are downloaded to the user’s machine. There they are meant to run inside a “sandbox”, which strictly limits their ability to read or write data to the PC. But the exploit shows that that has failed. Hackers have figured out how to exploit Java to install malicious software enabling them to commit crimes ranging from identity theft to making an infected computer part of an ad-hoc network of computers that can be used to attack websites.
While we can be assured that Oracle is working on fixes to security holes that hackers exploit, we do want to point out that there is a time lag in addressing the issues. In August 2012, Oracle did release a patch a month ahead of their scheduled patch. However, this happened after the Polish security alerted and received confirmation of 31 flaws. Only two were addressed prior to the patch.
Response time by Oracle improves when major players take major steps. In February 2013, Oracle only took one day to release a new version to address security vulnerabilities after Apple decided to block the latest update for Java 7. The “…Java Runtime Environment was being exploited by nefarious websites, and was so serious that the U.S. Department of Homeland Security warned users to disable the web plugin. In response, Apple disabled Java 7 through the OS X anti-malware system…” Mozilla Firefox has enabled what is referred to as a “Click and Play” tool so that the user gets an opportunity to accept playing the Java plugin or to leave it disabled on the web page.
What to Do
These reports are not encouraging. What we know to be commonplace in the computing world is that the more something is popular and used, the more it is a target for cybercrime. Such is the case with Windows being the target for viruses and Apple users thinking they were immune. So too is this true with Java. Logic dictates that having a replacement for Java may not be more secure, simply less targeted.
Many users rely on Java without even knowing it. One example would be playing a game such as ones offered with the Pogo site. These games require Java in order to be played. In January 2013, many Pogo Java games were asking the user for permission to run before they load. This was due to security measures implemented in the latest version of Java (version 7 update 11).
The challenge is to decide the best approach in terms of safety and functionality. There are two fundamental solutions. You can go without Java – disable it. Or you can forgo the risk, use Java and attempt to take all the required precautions. In this case, it means having recent and up-to-date Java upgrades with all the necessary security patches. There is one other approach that we will introduce here… use more than one browser.
Disable It: If you decide to go this route you need to first ask what will the result be and do I have an alternative in mind even if that alternative is to go without some functionality? As pointed out, Java is required for many applications and websites. For direction on disabling for your web browser, please refer to our article: Fix or Disable Java.
Use Java – Updates: As can be seen with the security risk examples included in this article, Java security exploits can and do occur. But if you are of the mind that other replacements for Java are just as likely to be the target of exploitation… then you may be deciding to stay the course. No need throwing caution to the wind. We recommend taking some precautions including having the most recent update and Java version. For our PC TuneUp Maestro users, the steps to updating Java is simple and easy. For more information refer to the following article: Fix or Disable Java.
With or without Java, or sometimes using Java, the choice is yours to make.

 There are several potential causes for a slow browsing experience. The plan is to identify the symptoms and then to systematically go through potential causes. We will attempt to rule out the ones less likely to be crippling your IE browser experience but are potential culprits all the same.
There are several potential causes for a slow browsing experience. The plan is to identify the symptoms and then to systematically go through potential causes. We will attempt to rule out the ones less likely to be crippling your IE browser experience but are potential culprits all the same.



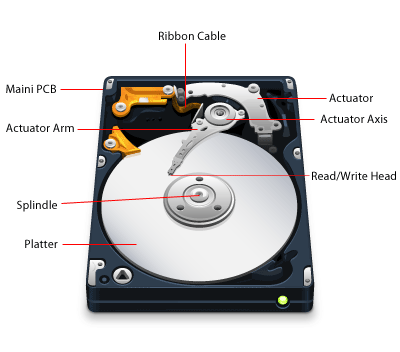
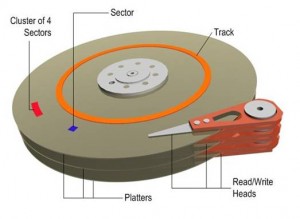 In this process, the data is stored magnetically like how a cassette tape works. In fact, both use the same recording techniques. The magnetic medium can be erased and re-written easily. If your PC needs data it would read the magnetic polarities on the platter. One side is a “0” and the other a “1” – this is referred to as binary data. Unlike cassette tapes, the Read/Write Head never touches the disk and consumer PC platters typically spin at 7,200 rpm; a speed of up to 3,000 inches per second. Also, much more information can be read to a disk in much smaller space than cassettes. Both speed and precision account for the ability to record so much data in such small magnetic domains.
In this process, the data is stored magnetically like how a cassette tape works. In fact, both use the same recording techniques. The magnetic medium can be erased and re-written easily. If your PC needs data it would read the magnetic polarities on the platter. One side is a “0” and the other a “1” – this is referred to as binary data. Unlike cassette tapes, the Read/Write Head never touches the disk and consumer PC platters typically spin at 7,200 rpm; a speed of up to 3,000 inches per second. Also, much more information can be read to a disk in much smaller space than cassettes. Both speed and precision account for the ability to record so much data in such small magnetic domains.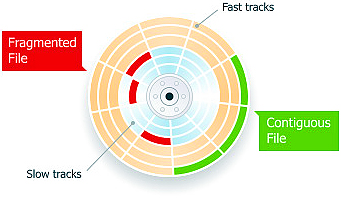
 Hard Disk Drive (HDD) performance is measured in the following manners:
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) performance is measured in the following manners: